Physical activity is one of the best practices for maintaining long-term health and well-being. Whether swimming, cycling, or just taking a walk, regular exercise may contribute to making your body stronger, support mental well-being, and reduce the risk of diseases linked to sedentary lifestyles. Integrating physical activity into your routine can foster lasting improvements in physical and emotional wellness. In this article, we focus on the key reasons physical activity is beneficial and how it might improve your long-term health.
Why Physical Activity Matters
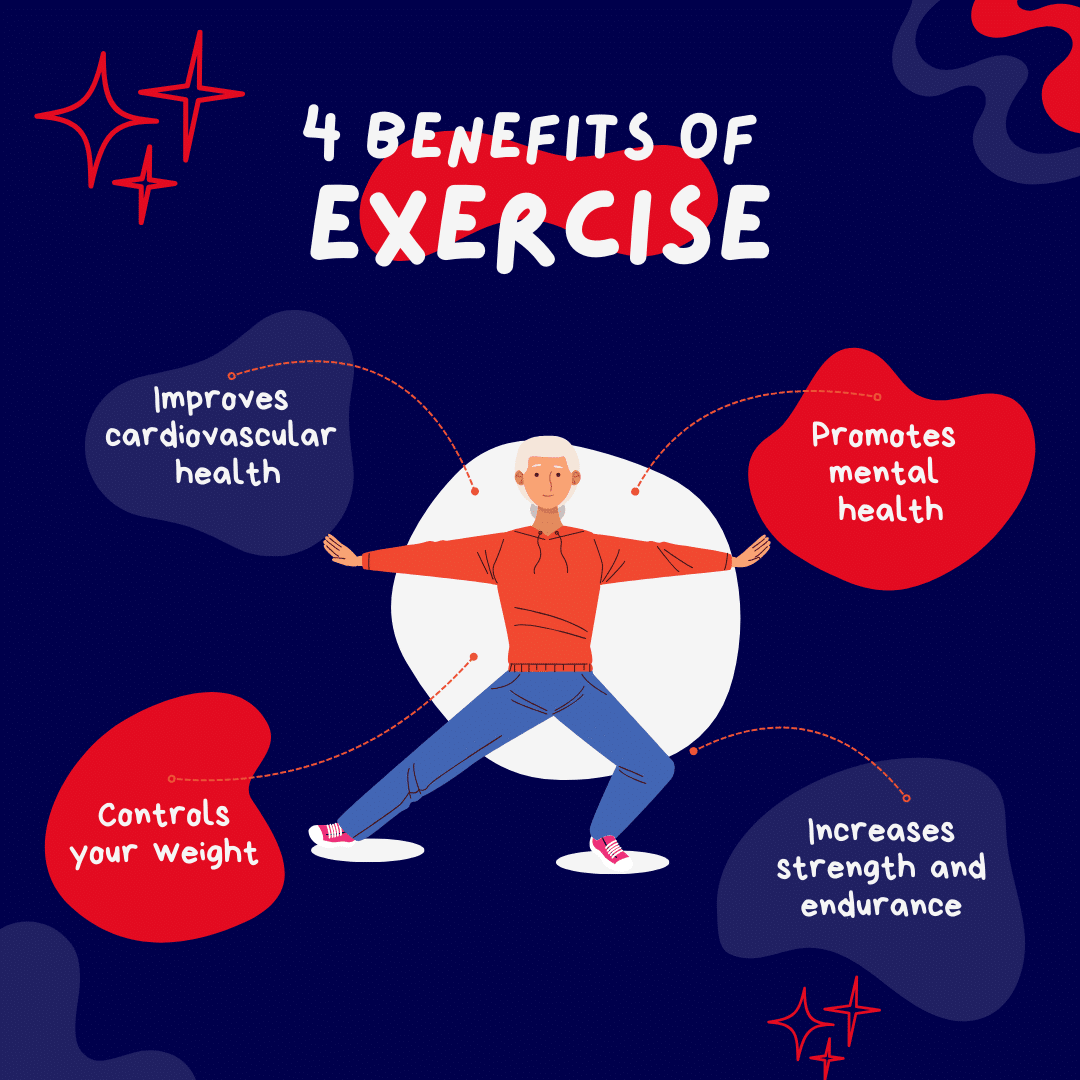
Regular physical activity supports optimal health and vigor. It can help reduce body fat, build muscle, and, more importantly, support the development of long-term wellness. Studies suggest that an active lifestyle is associated with a reduced risk of developing chronic illnesses such as heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. Additionally, it may enhance energy levels, mood, and mental clarity—essential benefits in today’s sedentary world.
For many individuals working desk jobs, incorporating regular exercise can be crucial to overall health, especially mental well-being. In settings like an intensive outpatient program (IOP), physical activity is often used as part of a comprehensive plan. These programs, designed for individuals seeking structured support while living at home, include exercise to support mood enhancement, anxiety reduction, and mental health recovery. For instance, just 30 minutes of brisk walking each day may help lower stress and contribute to the holistic approach IOPs take toward achieving wellness.
Some reasons why physical activity can improve your life include:
- Cardiovascular Fitness: Strengthens the heart and lungs, which may lower the risk of heart disease and improve circulation.
- Promoting Mental Health: Exercise releases endorphins, which can act as natural mood elevators and may help reduce stress, anxiety, and depression.
- Immune System Support: Moderate activity can encourage immune response and may lower the likelihood of illness.
- Improved Sleep: Regular exercise may support better sleep by helping you fall asleep faster and sleep more soundly.
- Bone and Muscle Strength: Physical activity supports bone strength, potentially lowering the risk of osteoporosis in later life.
Physical Activity and Mental Health
Exercise is recommended as part of a treatment plan that addresses depression and anxiety, supporting endorphin and serotonin release, both linked to mood elevation. Physical activity is a natural, healthy way to manage stress.
As a therapeutic tool, exercise is commonly integrated into mental recovery programs, including IOPs for severe anxiety or depression. It can help individuals establish routine and structure, potentially fostering a more effective recovery and encouraging healthy habits. Improvements in mood, self-esteem, and social connections are three critical elements of emotional recovery, and physical activity supports these areas in structured programs.
Symptoms linked to low physical activity may include:
- Anxiety: Exercise can help reduce anxiety by decreasing muscle tension and stress.
- Depression: Physical activity may encourage the brain’s production of mood-enhancing chemicals, supporting mental function.
- Stress: Exercise may lower stress hormone levels, providing a calming effect on the body and mind.
Incorporating Physical Activity into Your Life
For many, making time for physical activity can be challenging, but consistency is key to long-term benefits. Here are some tips for gradually increasing your activity level:
- Start small: Begin with 10–15 minutes of activity per day and gradually increase as your fitness improves.
- Set achievable targets: Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous activity weekly.
- Find activities you enjoy: Choose activities like dancing, swimming, or hiking to keep it engaging.
- Integrate fitness into daily life: Use stairs, walk or cycle to work, or plan regular workouts.
- Workout with a buddy: Exercising with friends can make the process more enjoyable.
- Join a fitness class or club: This can help keep you accountable and maintain a consistent schedule.
- Track your progress: Use fitness apps, smartwatches, or wearables to monitor steps, workouts, and progress over time.
Prevention of Chronic Diseases
One of the long-term benefits of regular physical activity is its potential role in preventing chronic diseases. Heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers may be prevented or managed with an active lifestyle. Studies suggest that active individuals have a lower risk of illness compared with those with sedentary lifestyles.
Some potential benefits of regular physical activity in chronic disease prevention include:
- Heart Disease: Physical activity may help reduce blood pressure, support healthy cholesterol levels, and strengthen the heart.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Regular exercise can assist in balancing blood glucose levels and may improve insulin sensitivity.
- Cancer: Research indicates that physical activity could reduce the risk of certain cancers, including colon and breast cancer.
- Obesity: Staying active can promote healthy weight management, which may lower the risk of diseases associated with excess weight.
Planning for a Healthy Future
Maintaining an active lifestyle is beneficial not only for short-term fitness but also for long-term health. Activities such as running, cycling, and strength training can support physical and mental health, potentially reducing the risk of chronic diseases and enhancing mental well-being.
Programs like an IOP for mental health focus on the appropriate levels of structured physical activity necessary for recovery and long-term wellness. This stage of recovery aims to bridge the physical, emotional, and mental aspects of well-being.
Summary
Incorporating regular physical activity into your life can be one of the most effective ways to support your overall health and well-being. Whether you’re looking to reduce stress, prevent chronic diseases, or enhance mental clarity, exercise plays a key role in long-term health.
By making small, consistent changes, you may experience the lasting benefits of an active lifestyle that supports both body and mind.
FAQs
- How many hours of physical activity should I aim for each week?
At least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity or 75 minutes of vigorous activity per week, combined with strength training exercises twice a week. - Can physical activity improve my mental health?
Yes, regular physical activity may help reduce symptoms of anxiety and depression, supporting a positive mood and mental clarity. - How does physical activity help prevent chronic diseases?
Physical activity can improve heart function, support healthy blood sugar levels, and promote weight management, potentially lowering the risks of chronic illnesses like heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers.
Disclaimer: This content is for informational purposes only and is not intended as medical advice, nor does it replace professional medical expertise or treatment. If you have any concerns or questions about your health, always consult with a physician or other healthcare professional.
Published by: Nelly Chavez